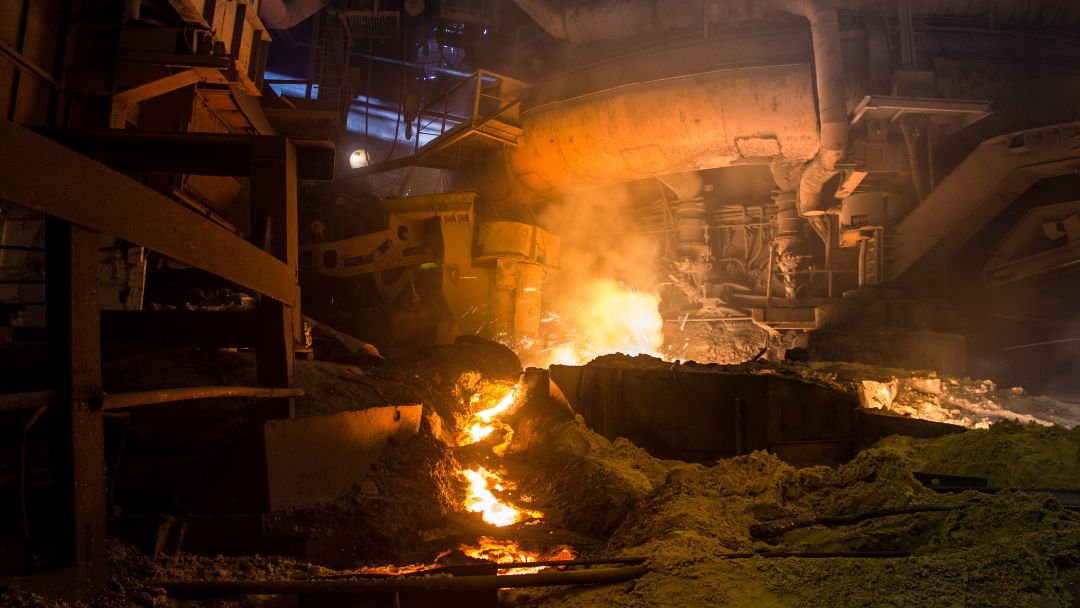
In the grand symphony of metal production, the blast furnace stands tall as a behemoth, breathing life into raw materials and birthing molten iron. This article delves into the intricate world of blast furnaces, unraveling their significance, core processes, applications, and the technological innovations that make them the heartbeat of the iron and steel industry Blast Furnace.
Decoding the Significance of Blast Furnaces
Blast furnaces are the crucibles of transformation, where iron ore, coke, and limestone converge to produce molten iron. Their significance lies in their unparalleled ability to efficiently extract iron from raw materials, a process that forms the foundation of the iron and steel industry. Blast furnaces are the linchpin of metal production, driving progress across diverse sectors.
Core Processes in Blast Furnaces
1. Iron Ore Melting:
- Iron ore, coke (a form of carbon), and limestone are charged into the furnace.
2. Combustion and Reduction:
- High-temperature air, or “blast,” is introduced, initiating the combustion of coke and the reduction of iron ore to molten iron.
3. Molten Iron Collection:
- The molten iron, being denser than the impurities, collects at the bottom of the furnace.
4. Slag Formation:
- Impurities from the iron ore combine with limestone to form slag, which floats on the molten iron and is tapped off.
Applications Across Industries
Blast furnace-produced molten iron finds applications across diverse industries, contributing to the production of:
- Steel Manufacturing: The primary raw material for steel production, molten iron undergoes further refining in steelmaking processes.
- Construction Industry: Utilized in the production of structural components, beams, and other construction materials.
- Automotive Sector: Employed for crafting vehicle components, including engine blocks, chassis parts, and structural elements.
- Machinery and Equipment: Applied in the manufacturing of various machinery and equipment components.
Technological Innovations in Blast Furnaces
Advancements in blast furnace technology contribute to enhanced efficiency and environmental sustainability:
- Hot Stove Technology: Preheating blast air using waste heat, increasing fuel efficiency.
- Pulverized Coal Injection: Injection of pulverized coal to replace a portion of coke, reducing carbon dioxide emissions.
- Top Gas Recovery Turbines: Capturing and utilizing excess gases for power generation, improving overall energy efficiency.
Considerations in Blast Furnace Operation
Efficient operation of blast furnaces involves careful considerations:
- Raw Material Quality: Ensuring the quality and composition of iron ore, coke, and limestone for optimal performance.
- Temperature Control: Monitoring and controlling temperatures to achieve efficient combustion and reduction processes.
- Environmental Compliance: Adhering to environmental regulations and implementing technologies for reduced emissions.
Conclusion
Blast furnaces are the titans of metal production, orchestrating the alchemical process that transforms raw materials into molten iron, the lifeblood of the iron and steel industry. Their significance, core processes, and continual technological advancements underscore their pivotal role in driving progress and innovation. As industries strive for efficiency and sustainability, blast furnaces remain at the forefront, forging the metals that shape the modern world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the significance of blast furnaces in metal production?
- Blast furnaces efficiently extract iron from raw materials, forming the foundation of the iron and steel industry, and are crucial in various metal production processes.
- What are the core processes in blast furnaces?
- Core processes include iron ore melting, combustion and reduction, molten iron collection, and slag formation.
- Where is blast furnace-produced molten iron used?
- Molten iron from blast furnaces is used in steel manufacturing, the construction industry, the automotive sector, and the production of machinery and equipment.
- What technological innovations have been made in blast furnaces?
- Innovations include hot stove technology for preheating blast air, pulverized coal injection for reduced carbon emissions, and top gas recovery turbines for improved energy efficiency.
- What considerations are important in blast furnace operation?
- Raw material quality, temperature control, and environmental compliance are crucial considerations for efficient blast furnace operation.